BIOL134 Week 8 Exam 2; Ch 28-34
- $35.00
- Question: Food passes through these structures in what order?
- Question: Which plants typically interact with soil bacteria to take advantage of biological nitrogen fixation?
- Question: What enzyme is released from the gastric glands to break proteins into peptides?
- Question: The haploid gametophyte being more developed than the sporophyte is a characteristic of .
- Question: Skeletal muscle is attached to bones by
- Question: ____ teeth are found in mammals and specialized for chewing.
- Question: The first line of defense is usually performed by
- Question: Kiwis belong to the group .
- Question: Which of the following are modifications that help frogs avoid predators?
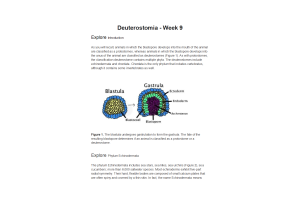
- Question: Annelids demonstrate protostomic development in embryonic stages and have their key characteristic of .
- Question: In dicots the inner seed coat is known as the .
- Question: You are working in a pathology lab, checking samples of different tissues for signs of disease. You get a new batch of samples from a patient: bladder, muscle, nerve fiber, and cartilage. The doctor forgot to tag the samples, but to your trained eye it is clear which is which.____Label them.
- Question: What features do leaves of aquatic plants have?
- Question: ____ muscle is found in viscera and is involuntary.
- Question: What is the difference between ruminants and pseudo-ruminants?
- Question: Only 10% of the cells in a human body are human – the rest are microbes that are important for health. A single human body can be described as a complex ecosystem. Plants also rely on distantly- related organisms and can be thought of as a small ecosystem. For each symbiont below, determine the result for the plant if they were missing.
- Question: Which hormones directly play an important role in plant defense?
- Question: In Caenorhabditis elegans, adverse environmental conditions can lead to the development of what kind of larva?
- Question: An ovary that is placed below other flower parts in an angiosperm is called
- Question: The perianth is comprised of
- Question: Primate features such as rotating shoulder joints and having big toes widely separated from the other toes is helpful for
- Question: Why do coniferous plants growing in cold climates have needle-like leaves?
- Question: What allows the bolus to enter the stomach?
- Question: In the phylum Mollusca, the distinguishing feature between the classes Aplacophora, Monoplacophora, and Polyplacophora is the number of
- Question: What percent of the animal kingdom is made up of organisms other than invertebrates?
- Question: A sheep is about to be fed alfalfa. What order would the alfalfa move through the digestive tract?
- Question: The number of petals in dicots is typically
- Question: Typically, organic matter makes up about ____ percent of the soil volume.
- Question: ____ bones are ones that have air spaces and struts so that they are lighter.
- Question: In monocots, the scutellum is another name for the _____ .
- Question: In scyphozoans, nerve cells are scattered all over the body and are sometimes found as clumps called
- Question: Where do plants obtain the chemicals that they need to sustain life?
- Question: Leeches belong to the class ____ .
- Question: Interveinal chlorosis can often be caused by a lack of
- Question: Celiac disease affects microvilli's ability to absorb nutrients. What tissue is affected?
- Question: Secretin is released in response to
- Question: In plant stems, the xylem and phloem form a structure called a ____ .
- Question: Nematodes typically have how many lips?
- Question: Leaves have air spaces to allow for carbon dioxide and oxygen to move into and out of cells for photosynthesis, which causes water to evaporate and creates greater tension on the mesophyll cells. How do xylem vessels and tracheids prevent collapse in these conditions?
- Question: In rotifers, the pharynx with jaw-like structures is known as the