CHEM134 Week 8 Midterm Exam
- $35.00
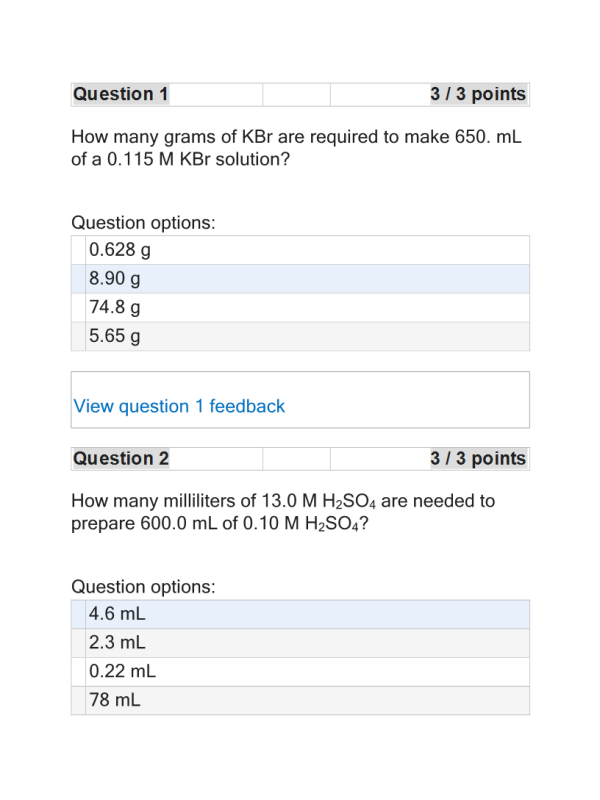
- Question: How many grams of KBr are required to make 650. mL of a 0.115 M KBr solution?
- Question: How many milliliters of 13.0 M H2SO4 are needed to prepare 600.0 mL of 0.10 M H2SO4?
- Question: In how many grams of water should 25.31 g of potassium nitrate (KNO3) be dissolved to prepare a 0.1982 m solution?
- Question: When two similar liquids mix to form a solution, the entropy of solution (ΔSsoln) is expected to be:
- Question: What is the mole fraction of ethanol in a solution made by dissolving 14.6 g of ethanol, C2H5OH, in 53.6 g of water?
- Question: How are the exponents in a rate law determined?
- Question: According to collision theory, which condition(s) must be met in order for molecules to react? 1) The reacting molecules must collide with sufficient energy to initiate the process of breaking and forming bonds. 2) A catalyst must be in contact with the reacting molecules for a reaction to occur. 3) The reacting molecules must collide with an orientation that can lead to rearrangement of the atoms.
- Question: The hydrolysis of tert-butyl chloride is given in the reaction below: (CH3)3CCl(aq) + H2O(l) → (CH3)3COH(aq) + H+(aq) + Cl (aq) If the rate law is: Rate = k[(CH3)3CCl], what is the order of the reaction with respect to water?
- Question: The decomposition of formic acid follows first-order kinetics: HCO2H(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g) The half-life for the reaction at 550 °C is 24 seconds. How many seconds does it take for the formic acid concentration to decrease by 88.8 %?
- Question: Concerning the rate law, Rate = k[A]2[B], what are appropriate units for the rate constant k?
- Question: If 0.617 mol PCl5 is placed in a 1.81 L flask and allowed to reach equilibrium at a given temperature, what is the final concentration of Cl2 in the flask? Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction?
- Question: Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction?
- Question: If the reaction quotient, Q, is greater than K in a gas phase reaction, then:
- Question: Given the equilibrium constants for the following reactions:
- Question: The decomposition of nitrosyl bromide is exothermic: 2 NOBr(g) ⇌ 2 NO(g) + Br2(g) Which of the following changes in reaction condition will shift the reaction to the left?
- Question: Which of the following is the most acidic solution?
- Question: Which one of these salts will form a basic solution on dissolving in water?
- Question: Consider a solution of 2.0 M HCN and 1.0 M NaCN (Ka for HCN = 6.2 x 10–10). Which of the following statements is true?
- Question: The OH– concentration in a 2.5 × 10–3 M Ba(OH)2 solution is
- Question: A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will react with the extra hydrogen ions from the HCl to keep the pH from changing?
- Question: What is the osmotic pressure in atm produced by a 1.02 M lactose (C12H22O11) solution at 25°C?
- Question: Calculate the freezing point of a lactose solution that contains 21.0 g of lactose (C12H22O11) per 100.0 g H2O (Kf = 1.86°C /m).
- Question: The rate constant for a particular reaction is 7.2 x 10-3 s-1 at 35 °C and 1.7 x 10-2 s-1 at 80 °C. What is the activation energy for the reaction?
- Question: For the following reaction:
- Question: If the equilibrium concentrations of [N2O4] = 4.3 x 10-2 M and [NO2] = 1.4 x 10-2 M, what is the value for Keq in the following reaction? N2O4 → 2NO2 (g) K = ?
- Question: Consider the following reaction: CO (g) + H2O (g) ⇌ CO2 (g) + H2(g) If you start with a mixture containing 1.00 mol of CO and 1.00 mol of H2O, calculate the number of moles of each component in the mixture when equilibrium is reached at 1000 °C. The mixture contains 0.43 mol H2?
- Question: If the pH of an arsenic acid H3AsO4 solution is 4.2, what is the concentration of the arsenate ion AsO43–?
- Question: Calculate the pH at the equivalence point when 50.0 mL of 0.10 M methylamine (CH3NH2) is titrated with a 0.20 M HCl solution.













-300x200.png)