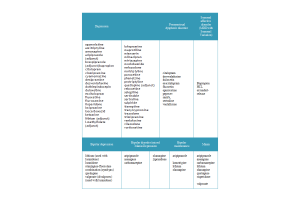
NRNP 6665 Week 8 Assignment; Study Guide Forum - Stereotypic Movement
- $15.00
A STUDY GUIDE FOR Student Name College of Nursing-PMHNP, Walden University NRNP 6665: PMHNP Care Across the Lifespan I Dr. Nataliya Ishkova- Volovets Date IMPORTANT FACTS Fig 1 Important Facts ➢Such movements can be hand waving, body rocking, or headbanging. ➢The movements can significantly impact regular activity or may cause physical bodily harm to patients with such conditions. ➢The rising cases of mental illnesses are critical concerns in nursing practice and psychiatry. It is essential to develop a framework to enable nurse students to develop relevant skills and competencies in the assigned mental health illness (Baizabal-Carvallo & Jankovic, 2017). ➢This study guide will explore various concepts associated with the selected mental illness. Signs and Symptoms ➢Based on the DSM-5, SDM is included in the neurodevelopment disorder; the diagnosis of the mental disorder should meet the diagnostic criteria, including the manifestation of clinical symptoms akin to SDM (Schertz et al., 2016). ➢The behavior is associated with significant interference with the normal activities; SDM sometimes leads to self-inflicted bodily injuries that may require medical interventions (He, Yi, & Yang, 2019). ➢Other mental health disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, such behaviors are not better accounted for. ➢Rocking ➢Headbanging ➢Nail-biting ➢Self-hitting ➢Picking at the skin ➢Hand waving or shaking ➢Hair pulling ➢Mouthing objects Fig 2: Symptoms of Stereotypic Disorder Differential Diagnosis Differential diagnosis is crucial in ruling out the possibilities of other mental health disorders that have symptomology that mimic those of the SMD (Schertz, Odom, Baggett, & Sideris, 2016). Fig 3: Known Differential diagnosis ➢The clinicians must rule out other psychiatric disorders in which repetitive behaviors are central features—obsessive-compulsive disorder, trichotillomania, vocal, and motor tics, and Tourette disorders. ➢The condition is often misdiagnosed as Tourette's. However, unlike SDM, which tends to begin at the age of two, tics of Tourette tend to have their onset between ages 6-7 (Baizabal-Carvallo & Jankovic, 2017). ➢Tourette is less bilateral and consists of less intense movement patterns for longer than Tourette's (Termine et al., 2021). ➢Individuals with tic disorders are less likely to display stimulated excitement. ➢Individuals with SMD are less bothered with the movements than those with tic disorders. ➢Clinicians should differentiate the SMD from other disorders based on presenting clinical symptoms (Stein & Woods, 2014). ➢Other of the most common mental disorders with characteristics or symptoms akin to SMD include: ➢Autism spectrum disorder ➢obsessive-compulsive ➢Related disorders, including other neurological and medical conditions. ➢Effective diagnosis of the psychiatric condition requires differential diagnosis and lab tests to facilitate accurate diagnosis and the administration of the most effective treatment for patients with confirmed cases of SMD (Termine et al., 2021). Incidence Fig 4: 10-15% Among Individuals with Intellectual Disability ➢The prevalence of stereotypic movement disorder is about 10-15% among individuals with intellectual disability within the general population. ➢SMD affects children with mental retardation, developmental disorders, and those who experience the effects of certain medications. ➢Other risks factors in the spread of SMD among the general population include social isolation and deafness (Stein & Woods, 2014)............ Continue