PHI 103 Week 15, Topic 7 Exam 3
- $35.00
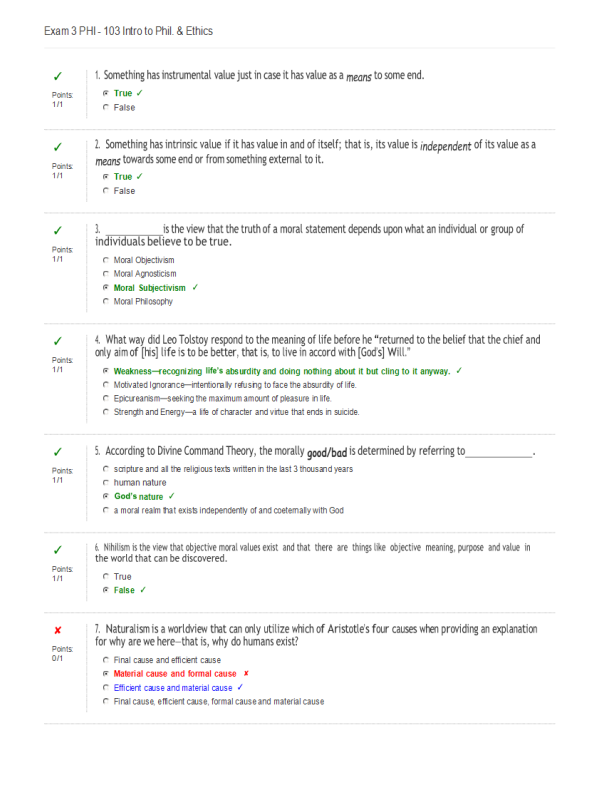
- Question: Something has instrumental value just in case it has value as a means to some end.
- Question: Something has intrinsic value if it has value in and of itself; that is, its value is independent of its value as a means towards some end or from something external to it.
- Question: _____ is the view that the truth of a moral statement depends upon what an individual or group of individuals believe to be true.
- Question: What way did Leo Tolstoy respond to the meaning of life before he “returned to the belief that the chief and only aim of [his] life is to be better, that is, to live in accord with [God’s] Will.”
- Question: According to Divine Command Theory, the morally good/bad is determined by referring to _____.
- Question: Nihilism is the view that objective moral values exist and that there are things like objective meaning, purpose and value in the world that can be discovered.
- Question: Naturalism is a worldview that can only utilize which of Aristotle’s four causes when providing an explanation for why are we here—that is, why do humans exist?
- Question: Virtue ethics evaluates a human action beyond the consequences and takes into consideration other things like attitudes, emotions, intentions, motivations, and character traits.
- Question: According to utilitarianism, a good will is not motivated to secure good ends and pleasures but, rather, is motivated out of duty to respect a moral law.
- Question: One approach to answering “What is the meaning of life?” is to answer the following kind of question.
- Question: The following statement is related to what sub-discipline of philosophy? “Acquiring knowledge of God’s goodness can be achieved, in part, by using our prior moral concepts and evidence for moral goodness.”
- Question: ____‘higher answer’– but none exists” Which two of Aristotle’s four causes is he appealing to?
- Question: One objection to Kant’s deontological ethics is that it denies that as you perfect your moral character, life becomes more enjoyable.
- Question: According to deontological ethics, the moral principle that motivates one’s decision is to do that which “produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people.”
- Question: _______ is the view that life's meaningfulness can be found metaphysically in God, which grounds the existence of objective values. It can be found epistemologically by offering a means to discover the necessary beliefs and right ways to live. It can be found relationally through being rightly related to God and having an eternally exiting soul, which can secure ultimate meaning.
- Question: Another horn of Euthyphro’s Dilemma says goodness resides in a moral realm that exists co-eternally and independently of God thereby making God unnecessary to ground the existence of goodness.
- Question: Euthyphro’s Dilemma is an objection to substance dualism.
- Question: According to Divine Command Theory, violating a divine command is an offense against God and this offense naturally causes humans to feel remorse and guilt.
- Question: Virtue ethics is the study of moral obligation and a theory of ethics that is not dependent upon the nature of human beings.
- Question: According to Divine Command Theory, the morally right/wrong action can be discovered by reference to ________ .
- Question: According to Kant, where is intrinsic goodness located?
- Question: According to Christianity, without the Holy Spirit's assistance, believers ______ .
- Question: One way to split the horns of Euthyphro’s dilemma is to say that goodness is neither (a) the result of God’s arbitrary will nor (b) something that exists co-eternally and independently of God but, rather, goodness is grounded in God’s nature—that is, God’s nature is the paradigm example of goodness.
- Question: Moral objectivism is the view that moral statements have a truth value and what makes a moral statement true is either (a) what an individual thinks is true or (b) what a group of individuals agree is true.
- Question: _____ is simply thinking hard about things that matter.
- Question: According to divine command theory, God’s commands do not give one any reason—whatsoever—to act morally.
- Question: According to Aristotle, Eudaimonia is the final human good, which is an activity of the soul manifesting its essential property, namely, rationality, in a way that allows one to be guided and informed by the virtues.
- Question: _____ and _____ are sometimes connected to whether or not there is meaning in life because if life has a "bad" ending then many think life is somewhat or wholly meaningless or absurd.
- Question: The three counterfeit candidates for human eudaimonia/happiness that Aristotle rejected because they have the wrong kind of value are _____ .
- Question: Some philosophers think there is no answer to the question "What is the meaning of life?" because there are only ways of thinking about how there can be meaning in life.
- Question: Some have argued, including Joshua Seachris, that the meaning of life question is asking for a narrative that addresses and explains things like ultimate origins, purpose, value, significance, pain and suffering, futility, ultimate ending, afterlife and judgment and can narrative these things—that is, explain them—in a way that corresponds to reality.
- Question: One horn of Euthyphro’s Dilemma says goodness is the result of God arbitrarily determining what’s good simply by willing it to be so, thus making morality arbitrary.














-300x200.png)
